Mood journal apps are transforming how we understand and manage our mental well-being. This exploration delves into the burgeoning market of these applications, examining their features, user experiences, and monetization strategies. We’ll uncover the strengths and weaknesses of leading apps, comparing their approaches to data visualization, personalization, and integration with other wellness tools.
The journey will reveal how these apps leverage technology to empower users on their path to better mental health.
From analyzing market trends and competitive landscapes to investigating user demographics and design principles, we will provide a holistic overview of the mood journal app ecosystem. We’ll also examine innovative features such as gamification, AI-powered insights, and secure data sharing capabilities, highlighting the potential for these apps to become indispensable tools in mental health management.
Feature Comparison of Mood Journal Apps
Choosing the right mood journal app can significantly impact your self-awareness and mental well-being journey. The market offers a diverse range of applications, each boasting unique features and functionalities. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting an app that aligns with your individual needs and preferences.
This comparison focuses on key features to help you make an informed decision.
Journaling Features
Different apps offer varying approaches to journaling. While most provide standard text entry, some incorporate multimedia elements to enrich the journaling experience. The inclusion of audio recording allows users to capture their emotional nuances more effectively, while image integration helps to visually document experiences and contextualize entries.
The availability of these options influences the depth and richness of the journaling process.
Integration with Other Health and Wellness Features
Many modern mood journal apps extend beyond simple journaling, integrating with other health and wellness trackers to provide a more holistic view of well-being. Sleep tracking, for instance, can reveal correlations between sleep quality and mood fluctuations. Similarly, activity tracking can highlight the impact of physical activity on emotional state.
This integrated approach allows users to identify potential patterns and triggers related to their mental health. For example, an app might show a clear correlation between insufficient sleep and increased reports of anxiety in the mood journal entries.
Data Visualization and Reporting
The ability to visualize and analyze journal data is a significant advantage. Effective apps offer various data visualization tools, such as charts and graphs, illustrating mood trends over time. These visual representations can quickly highlight patterns, potential triggers, and the effectiveness of coping mechanisms.
Detailed reporting features allow users to export their data for further analysis or sharing with healthcare professionals. Imagine a graph clearly showing a decrease in reported stress levels after starting a new exercise routine – this is the power of data visualization.
Personalization Options, Mood journal app
Personalization is key to ensuring consistent app usage. Customization options range from selecting themes to match personal preferences to setting reminders to encourage regular journaling. The availability of these features contributes to a more engaging and user-friendly experience, increasing the likelihood of long-term adherence.
For example, a user might choose a calming nature theme and set a daily reminder at 8 pm to reflect on their day.
Feature Comparison of Three Leading Apps
The following list compares three hypothetical leading mood journal apps, highlighting their unique selling propositions. Note that specific features and availability may vary depending on the app version and platform.
- App A: “MoodBloom”: Focuses on community support. Offers text, image, and audio journaling; integrates with sleep tracking; provides basic data visualization; offers limited theme options and customizable reminders. Unique Selling Proposition: Incorporates a supportive online community where users can connect and share experiences.
- App B: “MindTrack Pro”: Emphasizes in-depth data analysis. Offers text, image journaling; integrates with sleep and activity tracking; provides advanced data visualization and detailed reporting features; offers a wide range of themes and customizable reminders. Unique Selling Proposition: Provides comprehensive data analysis and reporting, ideal for users who want to track progress and identify patterns.
- App C: “InnerPeace Journal”: Prioritizes mindfulness integration. Offers text journaling, guided meditations, and breathing exercises; integrates with basic activity tracking; provides simple data visualization; offers a calming user interface and customizable reminders. Unique Selling Proposition: Combines journaling with mindfulness techniques to promote emotional regulation and stress reduction.
User Experience and Design of Mood Journal Apps
A successful mood journal app hinges on intuitive design and a positive user experience. This necessitates careful consideration of the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design principles, ensuring the app is both aesthetically pleasing and functionally effective in supporting users’ mental well-being.
The following sections delve into key aspects of UX/UI design within the context of mood journaling applications.
UI and UX Design Principles in Daylio
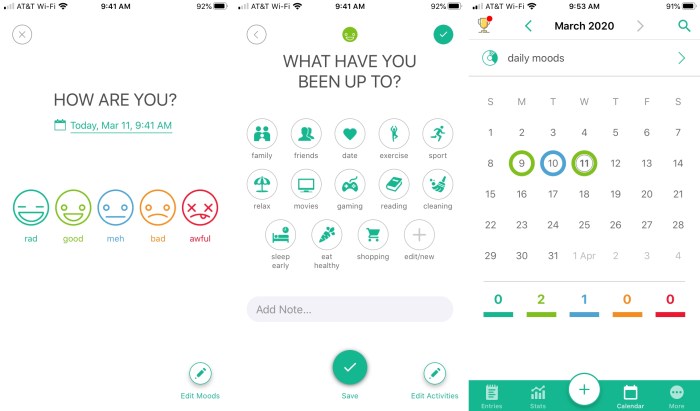
Daylio, a popular mood tracking app, exemplifies effective UI/UX design. Its clean, minimalist interface prioritizes ease of use. The primary screen presents a simple daily mood logging system, utilizing a selection of emojis to represent different emotional states. This visual approach reduces cognitive load and makes logging quick and straightforward.
Navigation is intuitive, with clear visual cues guiding users through the app’s features. The color palette is calming and consistent, reinforcing a sense of peace and tranquility. The overall design philosophy prioritizes simplicity and accessibility, making it suitable for users with varying levels of technological proficiency.
This approach is consistent with UX best practices emphasizing usability and user satisfaction.
Effective In-App Messaging and Feedback Mechanisms
Clear and helpful in-app messaging is crucial for guiding users and providing support. Daylio, for instance, uses gentle prompts to encourage daily logging and provides helpful tips on maximizing the app’s features. Feedback mechanisms, such as the ability to rate the app or provide suggestions, are essential for continuous improvement.
Furthermore, incorporating personalized feedback based on user data (e.g., suggesting additional journaling prompts based on logged moods) can enhance engagement and the app’s overall utility. Apps that offer a dedicated support section with FAQs and troubleshooting guides further enhance the user experience.
Prompt, informative error messages that guide users towards solutions, rather than simply stating the error, also greatly improve the user experience.
Improving the Onboarding Experience for New Users
A well-designed onboarding experience is critical for user retention. Instead of overwhelming new users with all features at once, a phased approach is more effective. Initially, focus on the core functionality – mood logging – providing clear instructions and visual cues.
Subsequently, introduce more advanced features gradually, perhaps through in-app tutorials or interactive prompts. A short introductory video showcasing the app’s benefits and core features can be incredibly helpful. Personalized onboarding based on user-selected preferences (e.g., preferred logging method or journaling style) could further enhance the user experience and increase user engagement.
The goal is to empower users to feel comfortable and confident using the app quickly.
Accessibility Features in Leading Mood Journal Apps
Accessibility is paramount for inclusive design. Leading mood journal apps should incorporate features like adjustable font sizes, high-contrast modes, and screen reader compatibility. Support for multiple languages expands the app’s reach to a broader audience. Furthermore, the ability to customize notification settings allows users to manage alerts according to their individual preferences.
Consideration of cognitive accessibility is also crucial, ensuring the app is easy to navigate and understand for users with cognitive impairments. These accessibility features ensure the app is usable by a wider range of individuals, regardless of their abilities or disabilities.
Mock-up of a New Feature: Mood-Based Music Recommendations
This feature integrates a music streaming service API to provide users with personalized music recommendations based on their logged moods. Visually, this could be implemented as a new section within the app, perhaps accessible through a tab labeled “Music.” Upon selecting a logged mood, users would be presented with a curated playlist of songs deemed suitable for that emotional state.
The visual design would be consistent with the app’s overall aesthetic, using calming colors and clear typography. Functionally, the feature would leverage mood-related s extracted from the user’s mood logs and use these to query the music streaming service’s API.
This feature could significantly enhance the app’s value proposition by providing a holistic approach to mood management, combining emotional expression with mood-appropriate music therapy.
Monetization Strategies for Mood Journal Apps
The success of any app, including a mood journal app, hinges on a well-defined monetization strategy. Choosing the right approach requires careful consideration of the target audience, app features, and long-term growth goals. Several models exist, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
This section explores these models and provides examples of their implementation.
Freemium Model
The freemium model offers a basic version of the app for free, while premium features are available through in-app purchases or subscriptions. This approach allows for a wide user base acquisition while generating revenue from a segment of engaged users.
- Advantages:Wider user reach, potential for viral growth through free access, opportunity for upselling premium features.
- Disadvantages:Requires a compelling free version to attract users, challenges in converting free users to paying customers, potential for a negative perception of the paid features if not perceived as valuable.
Implementing a freemium model for a new mood journal app could involve offering a free version with basic journaling capabilities, limited themes, and a restricted number of entries. Premium features could include unlimited entries, personalized reports, advanced visualization tools, a wider selection of journal prompts, and integration with other wellness apps.
For example, the free version might limit users to 5 entries per week, while the paid version offers unlimited entries.
Subscription Model
A subscription model provides access to all features of the app for a recurring fee (monthly, yearly, etc.). This ensures a steady stream of revenue, allowing for consistent app development and maintenance.
- Advantages:Predictable revenue stream, encourages user retention through ongoing value, supports continuous app improvements.
- Disadvantages:Requires a high-value proposition to justify the recurring cost, potential for user churn if the app doesn’t consistently deliver value, challenges in acquiring new subscribers.
Projected Revenue Model (Subscription-Based)
Let’s consider a subscription model with two tiers: a basic plan at $4.99/month and a premium plan at $9.99/month. Assuming 10,000 subscribers after one year, with 70% on the basic plan and 30% on the premium plan, the projected annual revenue would be:
(7000 subscribers
- $4.99/month
- 12 months) + (3000 subscribers
- $9.99/month
- 12 months) = $587,760
This is a simplified model, and actual revenue would depend on various factors such as marketing effectiveness, user acquisition cost, and churn rate. Successful apps like Headspace and Calm have demonstrated the viability of this model in the wellness app market, achieving substantial user bases and significant revenue through subscription fees.
In-App Purchases Model
In-app purchases allow users to buy individual features or content within the app. This model is often used in conjunction with freemium or subscription models.
- Advantages:Flexibility in pricing and offerings, potential for additional revenue streams beyond subscriptions, allows users to purchase only the features they need.
- Disadvantages:Can be perceived as disruptive or annoying if not implemented carefully, may lead to inconsistent revenue streams, requires careful design and implementation to avoid user frustration.
Marketing Strategies for Mood Journal Apps
Successful marketing involves a multi-pronged approach focusing on targeted advertising, content marketing, and app store optimization (ASO). This includes leveraging social media platforms (Instagram, Facebook, TikTok) to reach potential users, creating engaging content (blog posts, infographics) about mental wellness and journaling, and optimizing the app’s listing on app stores to improve its visibility and ranking.
Influencer marketing, collaborations with mental health professionals, and participation in relevant online communities can also significantly contribute to user acquisition.
Illustrative Examples of Mood Journal App Features
A successful mood journal app requires more than just a simple text entry field. To truly engage users and provide meaningful support, innovative features leveraging technology are essential. The following examples showcase how gamification, AI, and secure data sharing can enhance the user experience and effectiveness of a mood journaling application.
Gamified Journaling to Encourage Consistent Use
Consistent journaling is key to tracking mood patterns and identifying triggers. To incentivize regular use, a gamification system can be implemented. This system could award points for each journal entry, with bonus points awarded for completing entries daily or for including detailed descriptions of mood, activities, and thoughts.
These points could then be redeemed for virtual rewards such as unlocking new journal themes, customizing avatars, or accessing premium features like advanced analytics or guided meditations. A progress bar visually displaying the user’s streak and overall progress towards goals further enhances engagement.
Leaderboards could also be incorporated, allowing users to compete anonymously with others, adding a social element to the journaling process. The game mechanics should be designed to be intrinsically motivating, focusing on the sense of accomplishment and personal progress rather than solely on external rewards.
This approach fosters a positive feedback loop, encouraging users to continue their journaling habit.
AI-Powered Personalized Insights and Support
An AI-powered feature can analyze journal entries to provide personalized insights and support. This feature could employ Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms to identify patterns in the user’s mood, identify potential triggers for negative emotions, and suggest coping mechanisms based on established psychological techniques like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT).
For instance, if the AI detects a recurring pattern of negative mood associated with specific events or situations, it could suggest strategies for managing those triggers, such as mindfulness exercises or problem-solving techniques. The algorithm could also learn and adapt to the user’s individual needs and preferences over time, providing increasingly tailored support.
Privacy is paramount; all data processing should be conducted securely and anonymously, with user consent and control over data sharing. The AI should not offer medical advice but rather serve as a supportive tool that empowers users to manage their mental wellbeing.
Secure Sharing of Journal Entries with Healthcare Professionals
For users who wish to share their journal entries with a therapist or healthcare professional, the app should provide a secure and HIPAA-compliant method for doing so. This feature would require robust encryption protocols to protect user data during transmission and storage.
Users should have complete control over which entries they share and with whom, and the app should offer granular access control features. A secure messaging system integrated within the app could facilitate direct communication between the user and their healthcare provider.
The app should also clearly Artikel its data privacy policy and security measures, ensuring transparency and building user trust. This feature is crucial for users seeking professional support and requires adherence to the highest standards of data protection and confidentiality.
Ending Remarks
Ultimately, the success of mood journal apps hinges on a combination of effective design, robust features, and a user-centric approach. By understanding the market dynamics, competitive landscape, and user needs, developers can create applications that truly empower individuals to track, understand, and improve their mental well-being.
The future of mental health support may well lie in the continued innovation and accessibility of these valuable tools.